pleural effusion cat lymphoma
The most common causes for pleural effusion in all 380 cats were found to be CHF n155 408 and neoplasia n98 258. Tumors in the lungs or chest wall can lead to pleural effusion.

Fna Of Popliteal Lymph Node On A 9yr Beagle All Lymph Nodes Were Enlarged Lots Of Mitotic Figures Images Posted By Krist Vet Medicine Vet Tech Health Tech
Found with right congestive heart failure obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space lung lobe torsion neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating.

. Chylothorax has been reported in a cat after ligation of the left brachycephalic vein. Sixteen cases eight with chylous effusion had no underlying disease identified. 1 However solid pleural involvement is less common and is usually a secondary event.
The aim of this study was to evaluate in 20 cats presented with PE paired samples of serum and pleural. Pertinent findings included a high occurrence of pleural effusion with mediastinal lymphoma and other types of intrathoracic neoplasia pyothorax cardiomyopathy and feline infectious peritonitis virus infection. The most common presenting clinical signs include dyspnoea tachypnoea inappetence and cough with half of the cats presenting with pleural effusion at diagnosis.
Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma FIP nontraumatic diaphragmatic hernia vasculopathy uremic pleuritis hypoproteinemia and vitamin K antagonist toxicity. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. Either way the prognosis is not good.
EATCL type II is associated with indolent clinical behavior and prolonged survival time and. Primary pleural lymphomas are extremely rare and in a series reported by Burgener and Hamlin pleural plaques were seen in less then 4 of cases. How I Approach a Cat with Pleural Effusion.
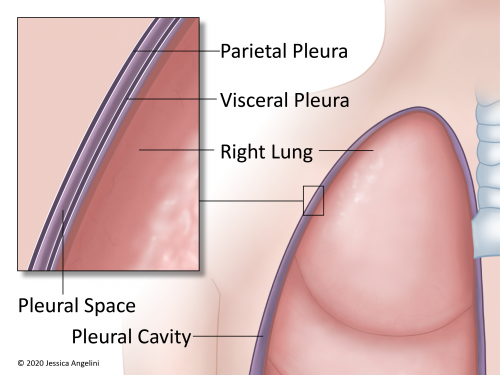
Two membranes line the thorax and lungs and the space between naturally has a small amount of fluid which helps to lubricate the lungs as he breathes in and out. Trauma is an uncommonly recognized cause of chylothorax in dogs and cats because the thoracic duct heals rapidly after injury and the effusion resolves within 1 to 2 weeks without treatment. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
In pleural effusion the lungs are floating in a chest that is full of fluid. In some cats infection with mutated coronavirus can lead to blood vessel damage which results in fluid leakage. Consists of small to intermediate-sized lymphoma cells which is consistent with current terminology that.
World Small Animal Veterinary Association Congress Proceedings 2018. In human medicine PEs are divided into only two categories. Classification of pleural effusion PE is central to diagnosis.
This type of effusion has been anecdotally associated with cardiac diseases in cats but studies are lacking. Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at the time of presentation. Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood.
The aim of this. Professor Sydney School of Veterinary Science University of Sydney Camperdown NSW Australia. When FIP affects the chest cavity pleural effusion results.
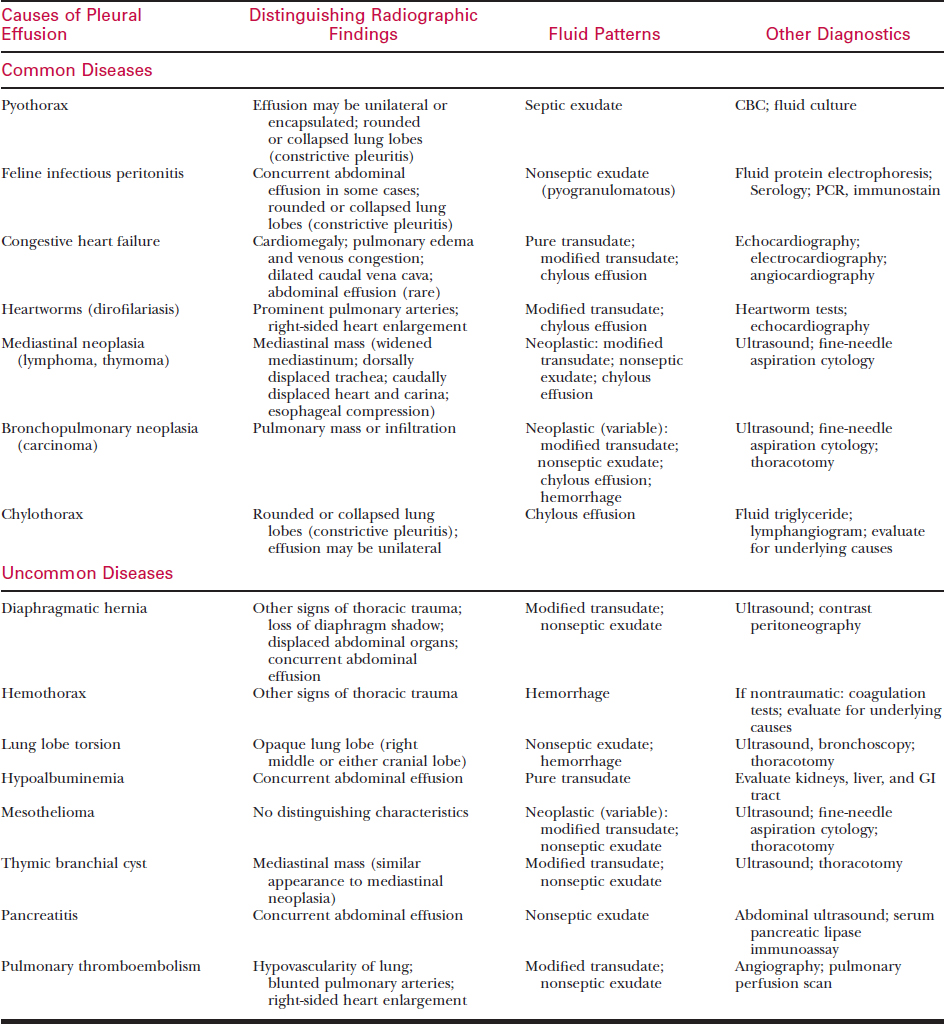
Form of feline lymphoma arises from diffuse mucosal associated lymphoid tissue MALT of the small. In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac. Pleural effusion in cats is a condition that causes an excessive amount of fluid to accumulate in the pleural cavity a space between the parietal pleura and the visceral pleura.
In this disease the conflicting fluid isnt inside the lungs but rather in the space that protects them. The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test. Ing 65 feline pleural effusions where diagnosis was.
Thoracic diagnostic imaging was performed in six cases and revealed pleural effusion and a diffuse thickening of the pericardium. Thoracic radiography is useful if clinical suspicion of respiratory disease but uncommon to see abnormal pulmonary parenchymal pattern perihilar or retrosternal lymphadenomegaly mediastinal mass or pleural effusion associated with alimentary lymphoma. Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity.
Objectives Non-chylous lymphorrhagic pleural effusions are transudative effusions with a predominance of lymphocytes. Cats with pyothorax and effusion secondary to trauma had the best prognosis for complete. This syndrome is caused by infection with a mutated form of a feline coronavirus.
Alterations in the cats blood pressure and protein content in the blood or the. Pleural effusion is an abnormal buildup of fluid up in the pleural cavity the thin fluid-filled space that lies between the lungs and the chest wall. We try to get these cats to survive 9-12 months.
This fluid occupies space within the chest keeping the lungs from expanding as fully as they should. Journal of small animal practice 2004 v45 no9 pp. Feline mediastinal lymphoma commonly occurs in young cats with a median age at diagnosis of three years and has commonly been associated with a positive FeLV status.
Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity which is lined by a membrane -- the pleural lining. Up to 25 cash back With pleural effusion youre usually dealing with one of two things- Lymphoma cancer or CHF congestive heart failure. Pleural disease in non-Hodgkins lymphoma is well documented and commonly presents with pleural effusions in 20 of patients.
Feline lymphoma historically has been highly associated with. This occurs in cats either because too little fluid is being absorbed in the pleural cavity or because too much fluid is being produced in the pleural cavity. Unfortunately says Margaret McEntee DVM professor of oncology at Cornell Universitys College of Veterinary Medicine it is the most frequently.
Feline lymphoma is a malignant cancer of the lymphatic system the exquisitely structured arrangement of internal organs and tissues that directly or indirectly influences virtually every aspect of a cats physical existence. Feline infectious peritonitis. Traditional veterinary classification has distinguished between transudates modified transudates and exudates.
Chronic inflammation may be associated with development of lymphoma. In the latter situations therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. Pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade in a cat with extranodal lymphoma Author.
Cats of the Siamese breed are overrepresented for both mediastinal lymphoma young cats and chylothorax. However they do not contain chylomicrons and therefore do not have the classical milky aspect of true chylous effusion.
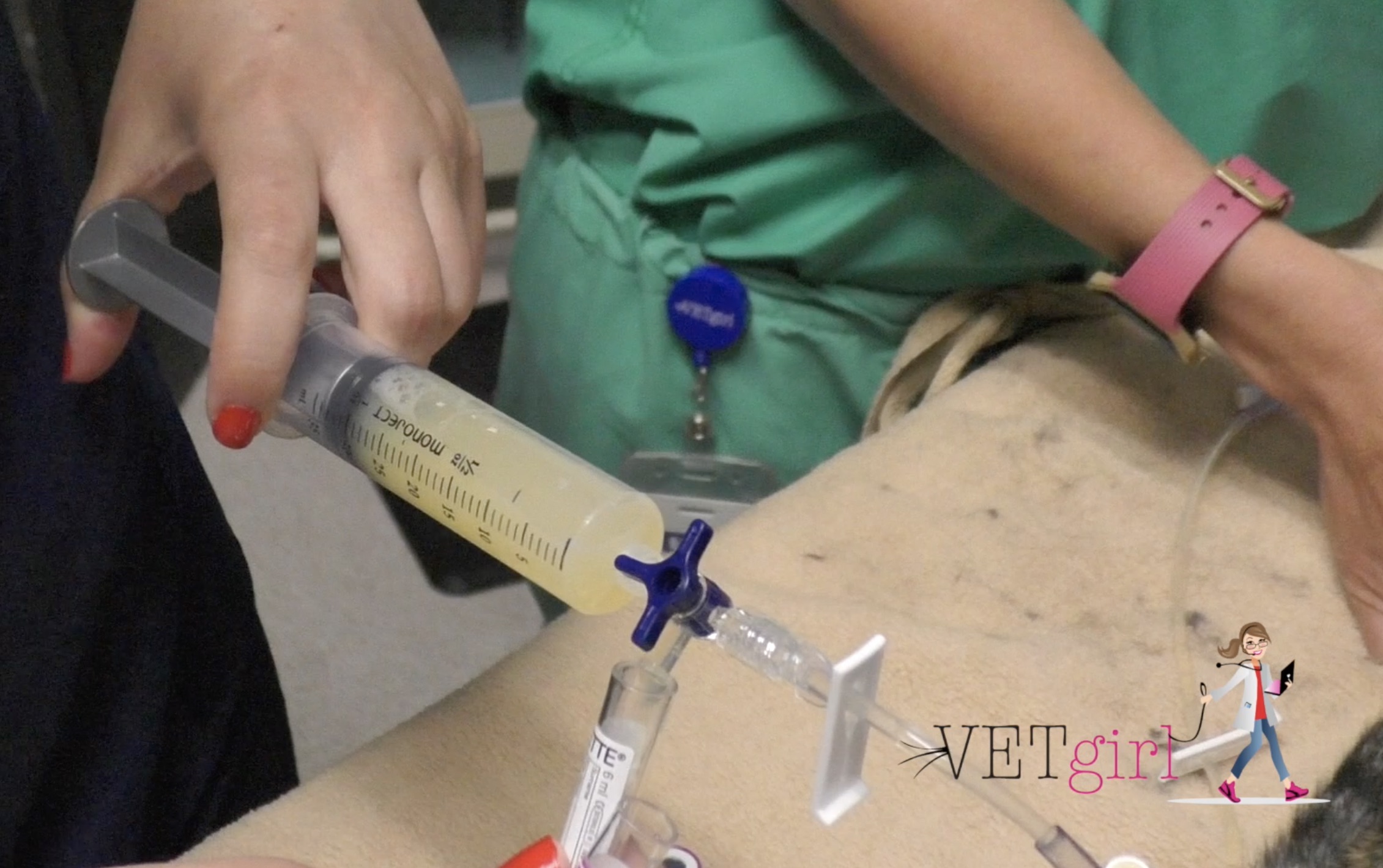
Causes Of Pleural Effusion In Cats Vetgirl Veterinary Continuing Education Blog

Fluid In Chest Pleural Effusion In Cats Petmd
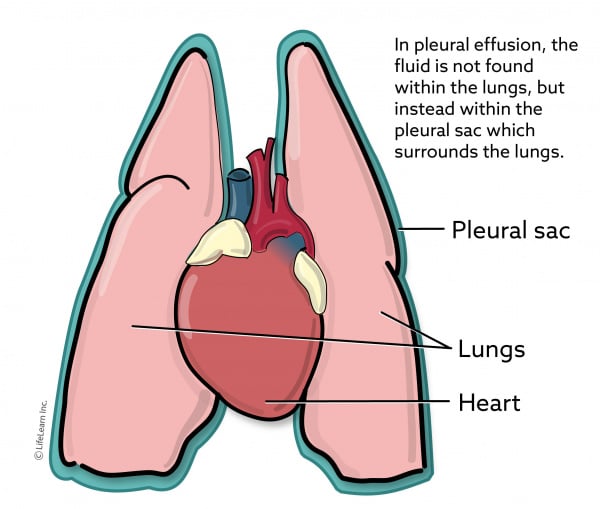
Pleural Effusion In Cats Vca Animal Hospitals
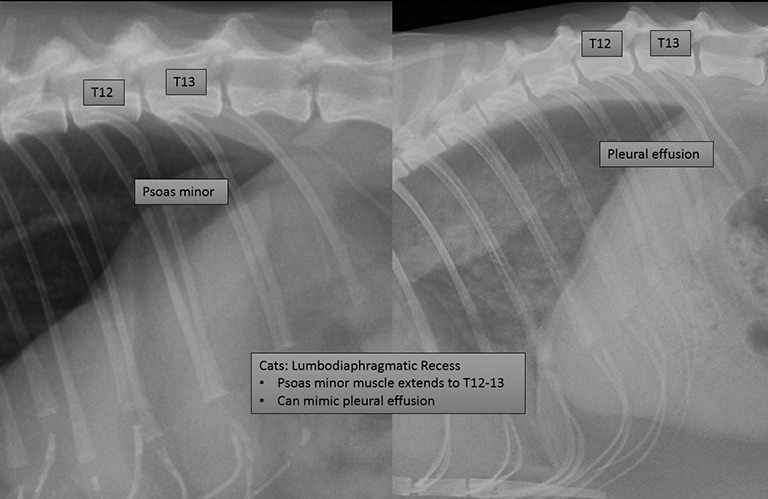
Thoracic Imaging Mediastinum And Pleura Mspca Angell
Indwelling Pleural Catheter Pleurx Oncolink
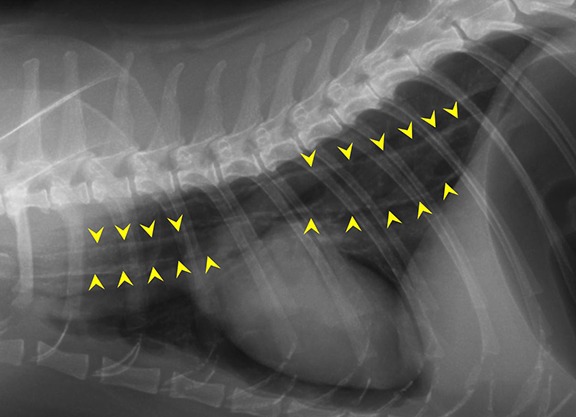
Thoracic Imaging Mediastinum And Pleura Mspca Angell

Chylous Effusion In A Cat Clinician S Brief

Lupus Erythematosus Le Cells Ask Hematologist Understand Hematology Hematology Microbiology Lab Medical Laboratory Scientist

Pin On Blood And Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital In Delhi
Pleural Effusion Treatment Management Approach Considerations Therapeutic Thoracentesis Tube Thoracostomy

Mediastinum The Mediastinum Is That Portion Of The Thorax That Lies Between The Right And Left Pleural Sacs A Thoracic Duct Thoracic Cavity Subclavian Artery
Modern Day Management Of A Unilateral Pleural Effusion Rcp Journals

Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat